kabschRotationMatrix
Below is a demonstration of the features of the kabschRotationMatrix function
Contents
clear; close all; clc;
Syntax
[Q]=kabschRotationMatrix(V1,V2);
Description
This function uses the "Kabsch" algorithm to determine the rotation tensor to best rotate the coordinates V1 to V2.
Examples
Example 1: Determine the rotation between two coordinate sets
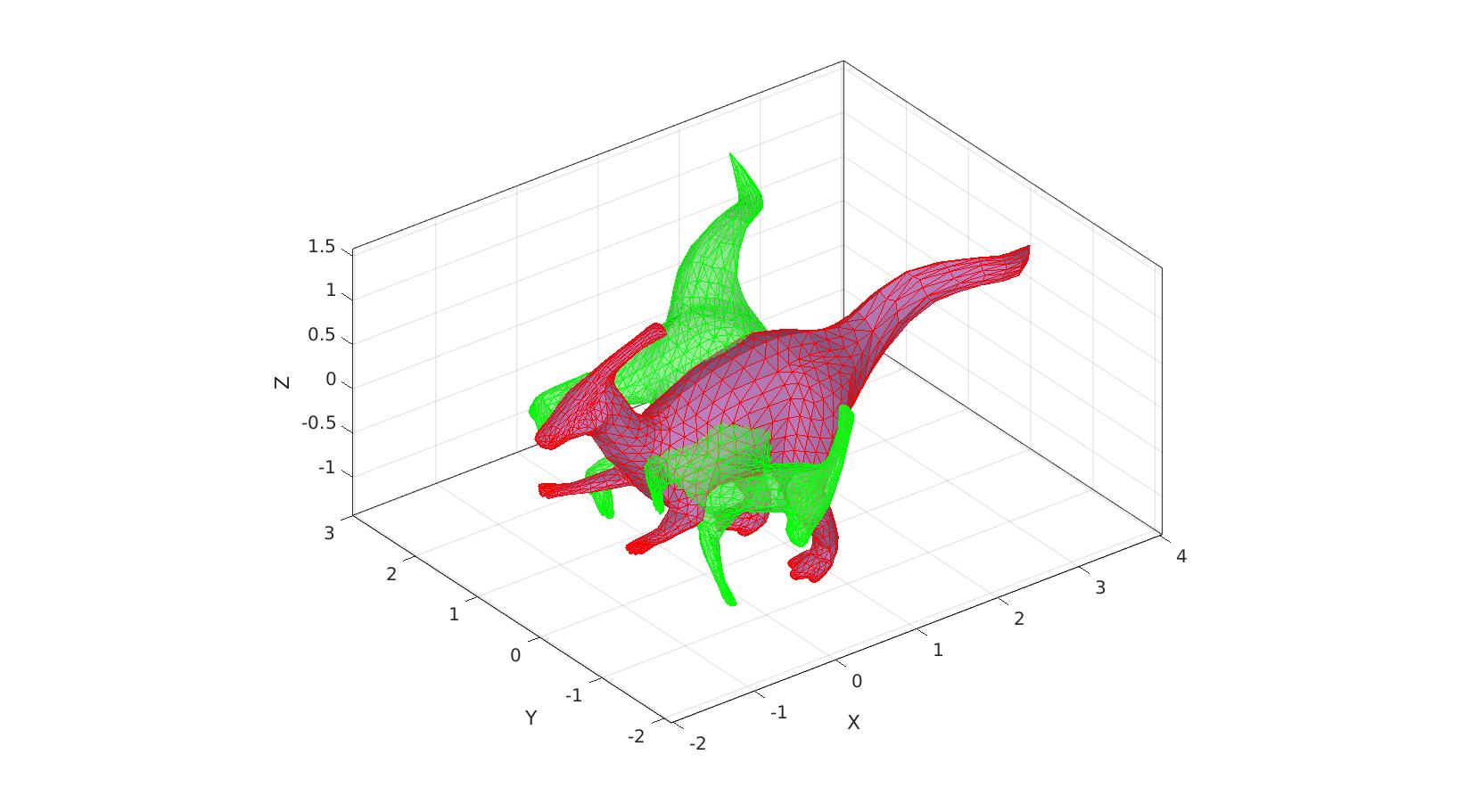
[F,V1] = parasaurolophus; % Example geometry for first coordinate set Qt = euler2DCM([0.25*pi 0.25*pi 0.25*pi]) %Example true rotation V2 = V1 * Qt'; %Create rotated second set
Qt =
0.5000 -0.5000 0.7071
0.8536 0.1464 -0.5000
0.1464 0.8536 0.5000
Using the Kabsch algorithm to determine the rotation matrix
Q = kabschRotationMatrix(V1,V2) %Determine rotation between V1 and V2
V3 = V2 * Q;
Q =
0.5000 -0.5000 0.7071
0.8536 0.1464 -0.5000
0.1464 0.8536 0.5000
Visualisation
cFigure; gpatch(F,V1,'bw','b',0.5) gpatch(F,V2,'gw','g',0.5) gpatch(F,V3,'rw','r') axisGeom; camlight headlight; gdrawnow;

GIBBON www.gibboncode.org
Kevin Mattheus Moerman, [email protected]
GIBBON footer text
License: https://github.com/gibbonCode/GIBBON/blob/master/LICENSE
GIBBON: The Geometry and Image-based Bioengineering add-On. A toolbox for image segmentation, image-based modeling, meshing, and finite element analysis.
Copyright (C) 2006-2023 Kevin Mattheus Moerman and the GIBBON contributors
This program is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or (at your option) any later version.
This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU General Public License for more details.
You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License along with this program. If not, see http://www.gnu.org/licenses/.